

They are calculated (usually by software) as a ratio of two components of the variance in a study. Both positive and negative values of T will give the same result, and P values are interpreted similarly for all T tests.į statistics are most commonly used as part of ANOVA. You can use this page to calculate the P value from T score statistics (and the correct degrees of freedom).
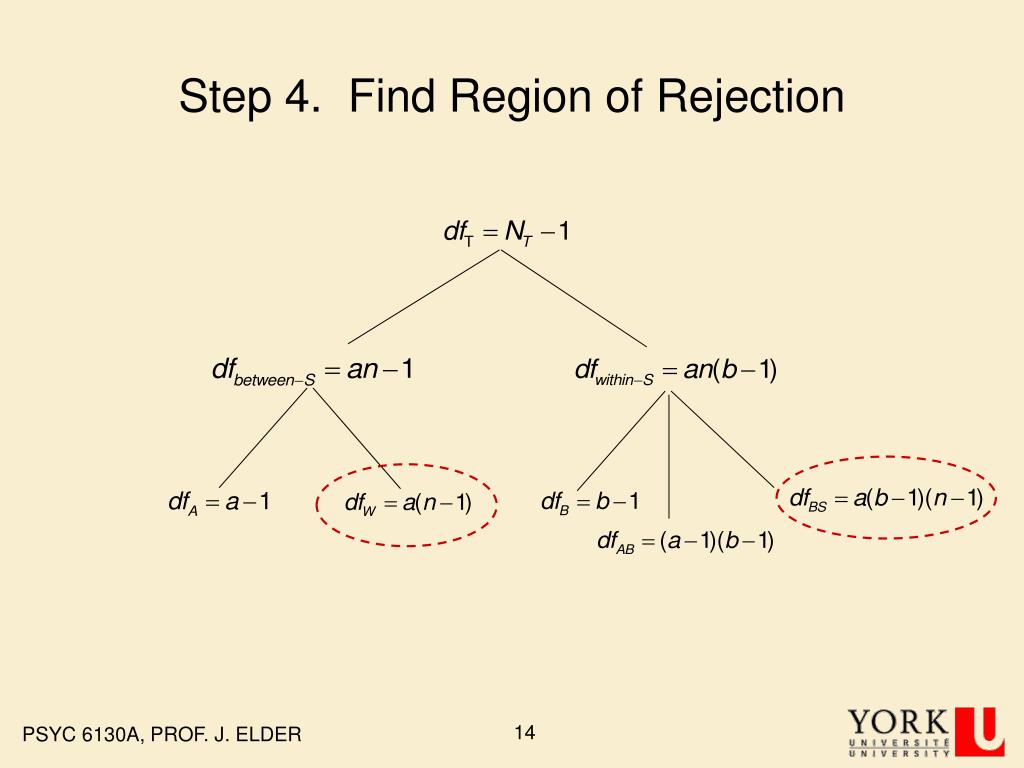
The basic form of a T statistic formula is: While there are plenty of similarities, the key difference is that while z scores standardize and test differences for proportions, T scores are used for testing mean differences from small samples. They are often confused with Z scores, and with large sample sizes, the two tests converge. T scores (or T statistics) are used to test the difference between a sample mean and another sample mean or some theoretical value. Entering your Z score as positive or negative will result in the same P value, because this test is two-sided. The most common formula to calculate a Z score involves the observation (X), the hypothesized mean (μ), and hypothesized standard deviation (σ):Įnter any number for Z to calculate the P value from Z score statistics. It is primarily used to test for differences between means for large samples. Z scores rely on the standard normal distribution (or Gaussian) which has a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. The Z score is a measure of how many standard deviations a data point is away from the mean. The closer to 0 it is, the stronger the evidence that you should reject the null hypothesis. Keep in mind, smaller is "better" when it comes to interpreting P values for significance. If it is equivalent or higher than the critical value, you fail to reject the null hypothesis. If the P value is less than that critical value, you reject the null hypothesis.
#Rejection region calculator f how to
Here are a couple examples of correct P value interpretations compared to several incorrect ways to state P value results.Ĭheck out this video on understanding P values for a quick refresher course if you are unsure about P values.īelow you can learn how to find P values for the most common statistical tests. P values are often considered the most widely misinterpreted concepts in all of statistics, often oversimplified to "the probability your outcome was due to chance". This calculator only uses two-tailed P values. They are reported as a decimal between 0 and 1, with some threshold (usually 0.05) deemed the significance critical value. While still widely used in scientific research, misuse of P values is at the heart of what is referred to as the " replicability crisis". P values help researchers avoid publication errors, specifically Type I Errors.

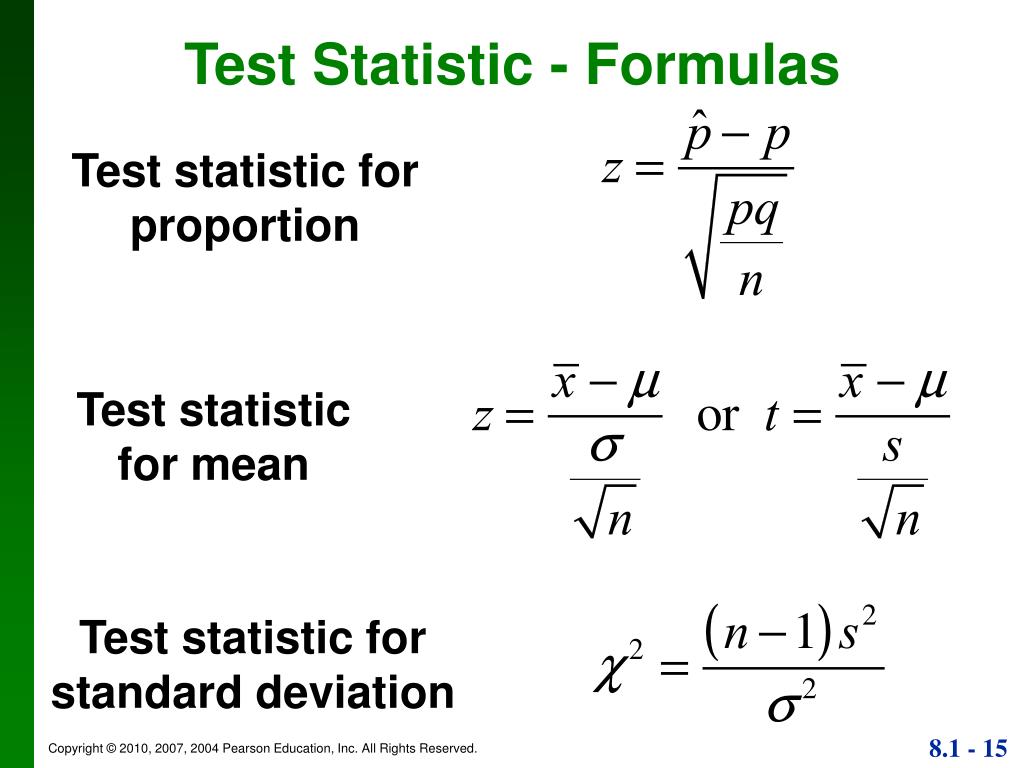
It is used to find the area between z = 0 and any positive value, and reference the area to the right-hand side of the standard deviation curve.P values (or probability values) are used in hypothesis testing to represent the chance that, assuming the null hypothesis is true, you could observe the result in your study or one even more extreme. Although there are a number of types of z-tables, the right-tail z-table is commonly what is meant when a z-table is referenced. Z-tableĪ z-table, also known as a standard normal table or unit normal table, is a table that consists of standardized values that are used to determine the probability that a given statistic is below, above, or between the standard normal distribution. The z-score has numerous applications and can be used to perform a z-test, calculate prediction intervals, process control applications, comparison of scores on different scales, and more. Where x is the raw score, μ is the population mean, and σ is the population standard deviation. The z-score can be calculated by subtracting the population mean from the raw score, or data point in question (a test score, height, age, etc.), then dividing the difference by the population standard deviation: z = Values above the mean have positive z-scores, while values below the mean have negative z-scores. The z-score, also referred to as standard score, z-value, and normal score, among other things, is a dimensionless quantity that is used to indicate the signed, fractional, number of standard deviations by which an event is above the mean value being measured. Use this calculator to find the probability (area P in the diagram) between two z-scores. This is the equivalent of referencing a z-table. Please provide any one value to convert between z-score and probability. Use this calculator to compute the z-score of a normal distribution.
Home / math / z-score calculator Z-score Calculator


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
